Rosetta

Rosetta Probe’s (Image credit: ESA)
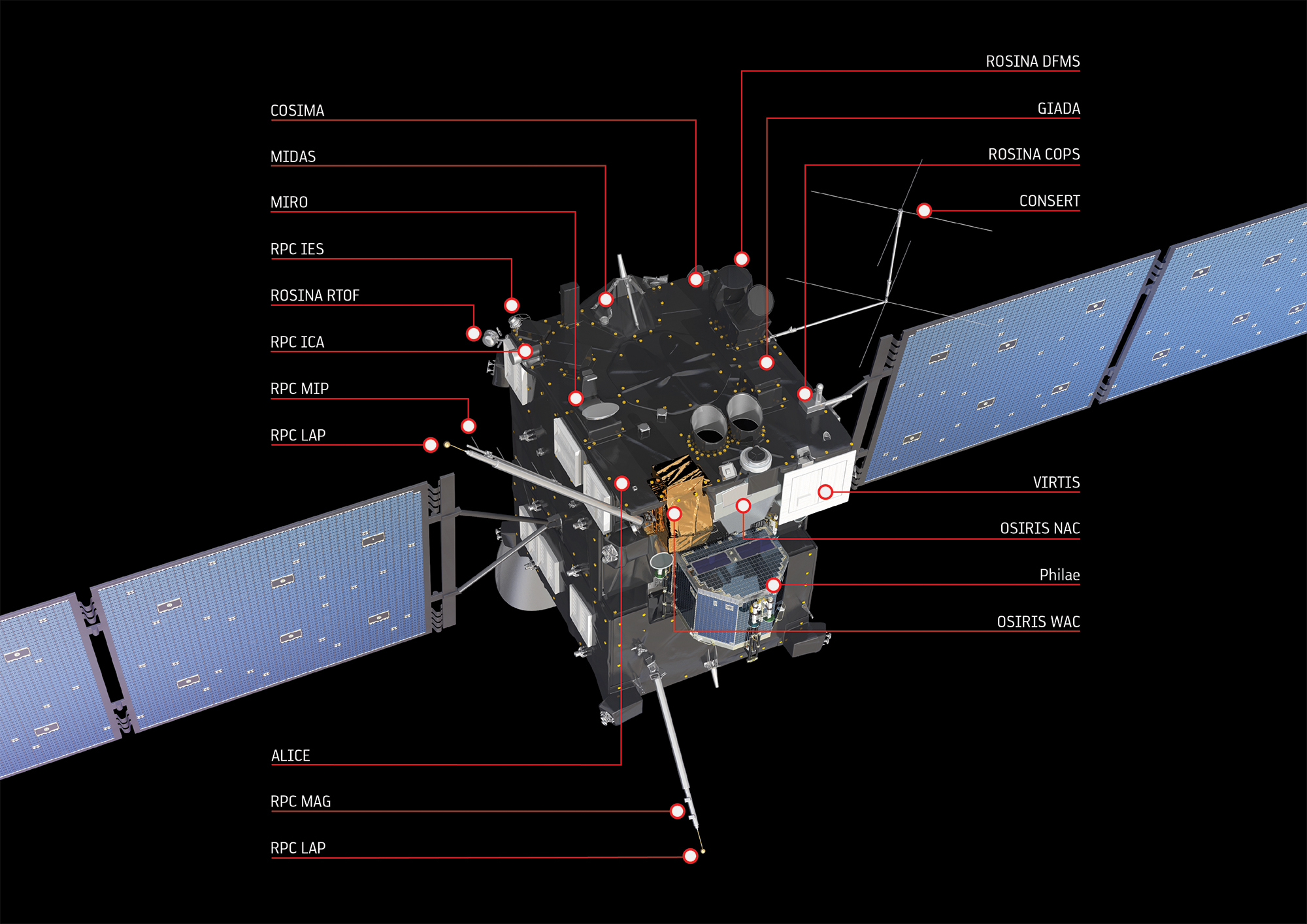
An ESA mission was launched in 2004 to visit the comet “67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko” to discover the history of comets and whether they played any part in bringing water to Earth. The spacecraft’s body is a 2.8 m x 2.1 m x 2.0 m (9.1 ft x 6.8 ft x 6.5 ft) with two solar panels, each having an area of 64 meter2 (688.8 feet) and a 2.2 meter (7.2 feet) high gain antenna.
The Rosetta mission marked many firsts: the first mission ever to chase a comet, the first mission ever to fly next to a comet while it approaches the Sun and the first to land a lander (Philae) on a comet. The lander weighs 100 kilograms (220 pounds) and is equipped with ten scientific instruments to perform in-situ measurements.
The spacecraft had a primary propulsion system and an additional 24 thrusters for course control.
Click here to learn more about other space missions
Related Links