In 1915, Albert Einstein published his General Theory of Relativity. According to this theory, gravity is not a force, as it had been considered since Newton published his work on gravity. Einstein viewed gravity as the bending of space-time itself.
When we put a massive object in space, it creates a curvature in the fabric of the cosmos. Objects nearby the massive one follows the geodesic path in that curvature. Thus, an illusion, that the objects are attracting each other, is created. That is why when you throw a ball away from Earth, it returns backs, following that geodesic path, not because of some mysterious force of attraction, objects possess.
Geodesic denotes the shortest possible line between two points on a sphere or other curved surface like earth
This idea revolutionized our understanding of the Universe. It opened up directions to explore the Universe, to know what is the nature of nature. Since General Theory of Relativity was first published in 1915, it made many predictions, and they have been proven.
The idea of Black Holes or the Dark Angels came from Einstein’s theory of general relativity. According to General Relativity, the more massive an object would be, the more curvature it will create in space-time. Imagine a ball on a trampoline, a smaller ball will create a small curvature, while a massive one will create a larger curve. Hence, the more mass you add to an object, its gravitational influence will increase.
In the case of our Earth, it bends space around itself so that the moon remains orbiting it. For any object in the vicinity of any celestial body, it needs some energy to escape from its gravitational influence. For example, in the case of Earth, the object must have a kinetic energy of 11.19 km/s to escape. This velocity, with which the object can escape another object’s gravitational influence and enter into space, is called Escape Velocity. It wholly depends upon the mass of the celestial body, from which you are trying to escape. As the Sun is massive than Earth, its escape velocity is 615km/s, which means you need to cover 615km in just one second.
In 1916, one year after the publication of General Relativity, a scientist named Karl Schwarzschild worked out a solution of general relativity, which predicted the existence of an object, so dense and so massive, that it can curve the space around it to infinity. Well, Schwarzschild’s solution didn’t give the modern definition of the black holes, but it paved a way towards further exploration of this mysterious object.
The first modern definition of black holes came from the work of David Finkelstein in 1958. Black holes are defined as the region in space-time from which nothing, not even light, can escape. Remember, light is the fastest thing in the Universe, and its speed is the Universe’s speed limit. American astronomer John Wheeler coined the term black hole in 1967. It had been considered a result of mathematical curiosity until 1971, when the first black hole, Cygnus X-1, was spotted in Cygnus’s constellation. It led scientists to have more faith in Einstein’s general relativity. It predicted gravitational waves, which were discovered by the LIGO observatory in 2015. Four years later in 2019, EHT (Event Horizon Telescope) team captured a black hole for the first time.
When Einstein was working on his Relativity theory, the nature of the Universe was considered static. But his equations were predicting an expanding universe. So, he introduced a term called Cosmological Constant, which later he called his Biggest Blunder.
In the 1920s, when Edwin Hubble discovered that the Universe is expanding, Einstein rearranged his equations with that new term. Today, it explains the expansion of the Universe, a problem in physics called Dark Energy. It is considered a mystery because still, we don’t know why the Universe is expanding. After Edwin Hubble made this discovery, scientists thought that the expansion of the Universe is due to the Big Bang. Imagine a blast, in this scene, you will see that the particles would be moving away from the center. Scientists thought that the same is happening with the Universe. Galaxies are receding away because of that initial thrust due to the Big Bang’s energy. With time, it must slow down due to gravity. But the problem began in 1990s when astronomers observed the Universe again. The observation astonished the scientists; instead of slowing down, the Universe expansion rate increased. There was no known reason which can trigger the expansion rate. There must be something else that is causing the Universe to expand at ever fasting rate. This unknown force that is causing the Universe to expand is termed as Dark Energy.It is estimated that this energy comprises 68% of the Universe. On the one hand, discoveries were proving Einstein right but some new ideas were popping out at the same time which were making scientists doubt this theory.
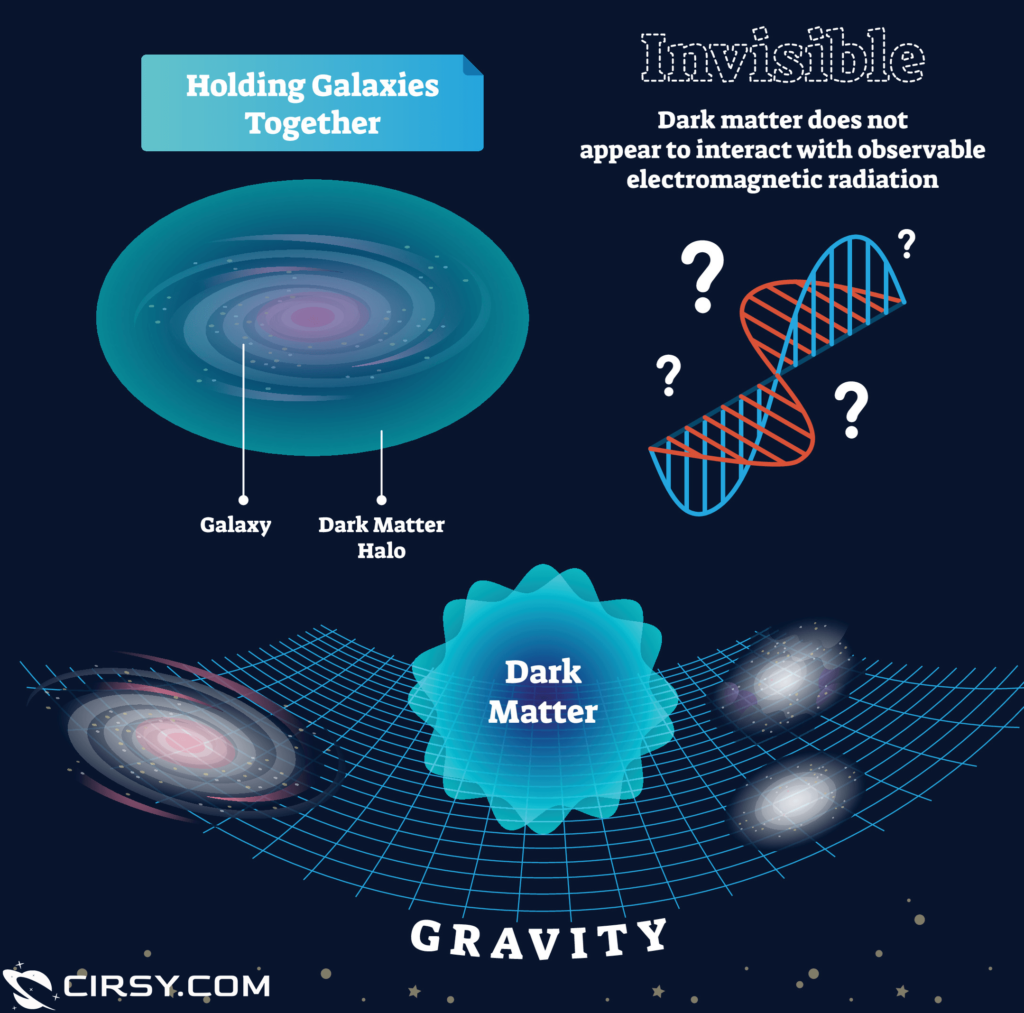
In the 1970s, Vira Rubin and Kent Ford, observed something very bizarre, something which shouldn’t be happening. They observed our nearby galaxy, Andromeda. Their observations showed that the stars away from the galaxy’s center were moving as fast as the nearby ones. If they are moving fast at such a huge distance from the center of the galaxy, they must fly apart.
Imagine a spinning wheel, if the wheel is rotating slowly and you put some water on it, it will remain stick to the wheel. But when you move it fast, the water on the wheel will fly apart. The same thing should be happening in the case of galaxies, but it is the opposite there. The stars instead of flying away remain there. This can happen only if there is some extra matter whose gravity is holding the stars back. But astronomers saw no matter there, which can support this phenomenon. General relativity can’t explain this.
Today, scientists call this problem “Dark Matter”, which cannot be observed directly but is there. Scientists says that every galaxy have this unknown source of gravity. And in the early Universe, it must have played an important role in the formation of galaxies.
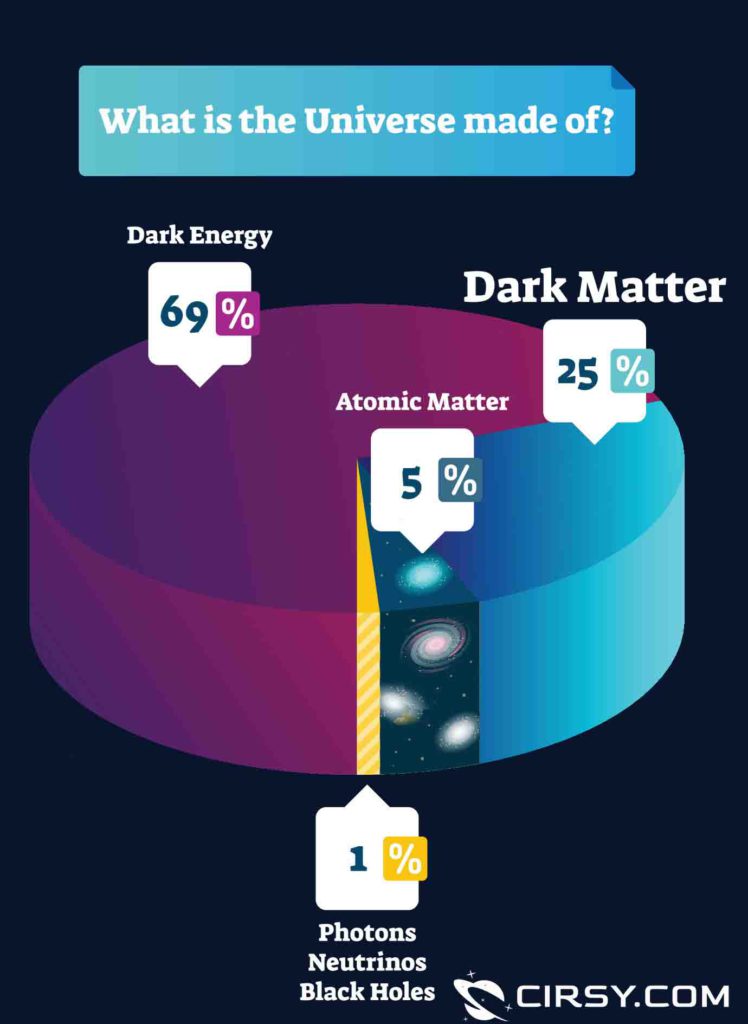
According to estimations, 27% of the Universe is made of Dark Matter. This is scary that the trillions of stars and planets, the whole of the observable Universe we can see, make only 5% of the entire cosmos. Some scientists think that this shows that general relativity is incomplete, and we need to modify it.
In 2010, Erik Verlinde, a string theorist, suggested that there is no invisible matter (Dark Matter) there to hold the stars back, and our theory of gravity cannot explain this. His new theory of gravity, called Emergent Gravity, predicts the exact same deviation of motions usually described by inserting dark matter in the story. He thinks that general relativity is still incomplete, and we have to modify it. He is working on it and hopes to find a solution soon.
It shows how dark matter is the failure of general relativity. It has limits, the same which happened with Newton’s theory of gravity, which wasn’t able to describe the nature of the Universe at a large scale. Another aspect that led scientists to doubt the theory is related to the objects predicted by the theory itself, i.e., black holes. Black holes are created when a star, at least three times massive than our Sun dies with a spectacular explosion called Supernova. This explosion spread matter into the Universe but the core remains there. The core of massive stars collapses inward upon itself, creating a point with infinite density and zero volume. This point is called the Singularity. What is Singularity? What happens to matter in the Singularity? Scientists don’t have any answers to these questions. And general relativity stops working inside a black hole. Einstein’s field equations break as scientists try to apply them. Time doesn’t exist there. Space makes no sense at all. Maybe, the worst of all is that does not fit with an even more accurate theory, Quantum Mechanics. Quantum mechanics describes the behavior of matter at an extremely small scale. Yet, there is no theory that describes how gravity works at the quantum level. Whenever both the theories are tried to combine, disaster occurs. For example, general relativity states that mass bends space-time, as an electron has a mass, does it bends space-time? From Quantum Mechanics, we know that quantum particles like an electron don’t have a certain position. They are at multiple locations at the same time. So, does gravity is also at different locations at the same time? During the double-slit experiment, an electron passes through both the holes at the same time. Where is gravity here? Einstein’s general theory of relativity fails and can’t answer these questions. Both the theories are doing a great job at their places, but they are incompatible with each other. But in places like Black holes, they must work together. The search for unifying both theories is still going on and there also different candidates like M-theory and Loop Quantum Gravity, but they are still not proven.