Rockets are used to launch satellites and Space Shuttles into space. Their powerful engines allow spacecraft to be blasted into space at incredible speeds, putting them into the correct orbit.
Cardboard tubes can be turned into all sorts of crafts. Rockets are a popular item for kids; you can make one using a cardboard tube. This project is a creative DIY for the kids to do with materials easily found at home, such as cardboard, glue, and colored paper.
Difficulty: Medium
Average Time: 10-15 Minutes
MATERIALS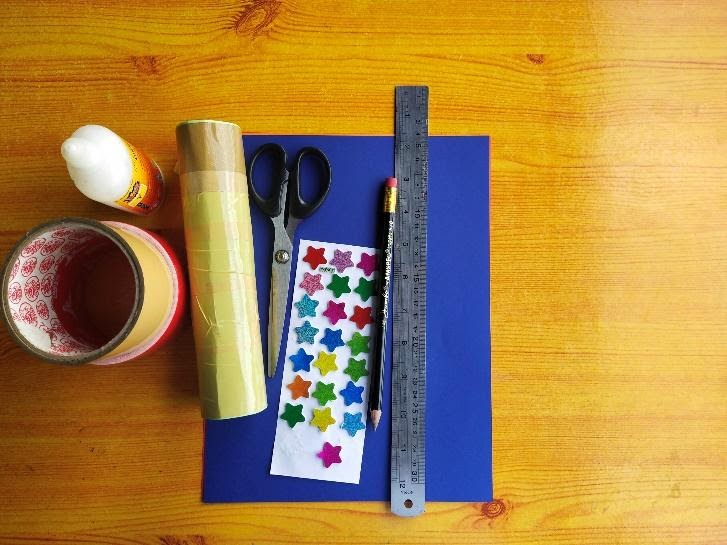
Cardboard tube
Scissor
Design Stickers
Construction papers(different colors)
Glue





DISCUSSION
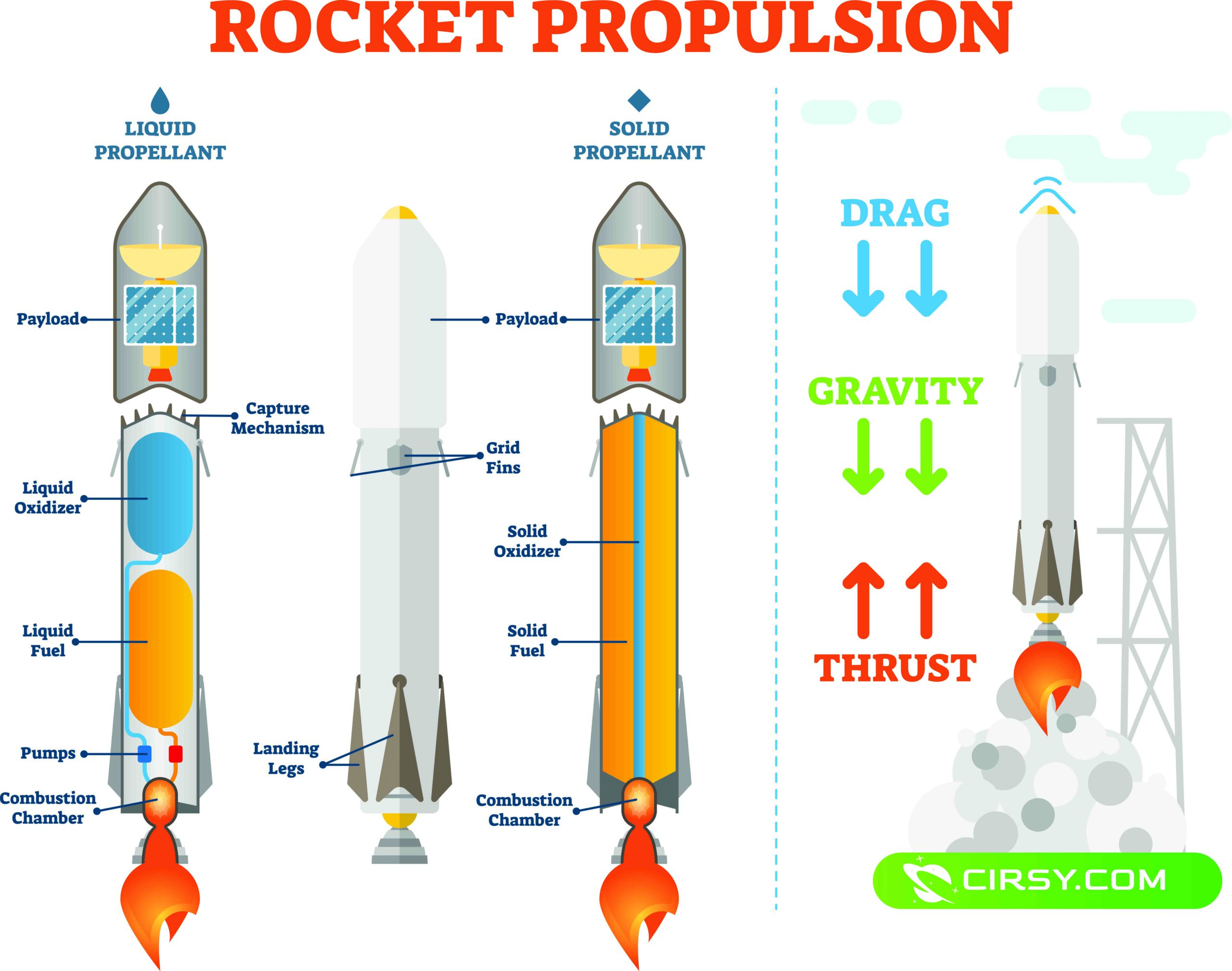
Rockets are designed to withstand the force of the powerful thrust generated from the rocket boosters. The bigger the size of the rocket, the more durable materials are needed for construction.
The rocket’s top part is usually in a pointed cone shape for reduced air drag during the liftoff. The lower part of the rocket usually has pointed nozzles and bolted to the cylindrical body. These nozzles are widened or narrowed depending on the size of the rocket. The size of the nozzle controls the thrust generated by the propellant or fule used by the rocket.
Rocket propellants may be either be liquid or in solid form. Liquid fuel uses an oxidizing agent to ignite. This propellant usually uses pumps and valves to mix the liquid fuel and oxidizing agent to ignite, making the rocket active and producing thrust. Liquid propellant rockets are more controllable compared to sloid rocket fuels. Once the fuel starts to burn in Solid rocket Fuels, the burning is uncontrollable.
Rockets work based on Newton’s 2nd and 3rd laws of motion. In a simple statement, these laws state:
Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion: Force is equal to mass times acceleration.
Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion: For every action, there is always an opposite and equal reaction.
According to the second law, If we apply a force to the rocket, it will accelerate. This force in rocketry is called the “thrust” of the rocket engine. The greater this force, the faster the rocket will accelerate. The mass also affects acceleration. A small, lightweight rocket accelerates faster than a larger, heavy rocket when the same thrust force is applied.
Newton’s Third Law is used to describe the thrust generated by a Rocket engine.


